Large Language Models are Zero-Shot Reasoners (May 2022)
Overview
Language models have shown impressive capabilities in few-shot learning, where they learn from a handful of examples. However, this paper from early 2023 shows that large language models (LLMs) can perform complex reasoning tasks with zero examples - they just need to be asked to Think Step-by-Step
Background
Traditional approaches to getting LLMs to solve complex reasoning problems involved showing them several examples with step-by-step solutions (called Chain-of-Thought Prompting or CoT).
This new research shows that by simply adding the phrase "Let's think step by step" before asking for an answer, LLMs can break down and solve complex problems without any examples.

Figure 1: Example inputs and outputs of GPT-3 with different prompting techniques.
a) Zero-shot CoT uses more examples than few-shot CoT
b) Few-shot CoT requires no examples while zero-shot CoT needs many
c) Zero-shot CoT only needs the prompt "Let's think step by step" while few-shot CoT needs example solutions
d) Zero-shot CoT only works on simple problems
Technique - Two Staged-Approach
Let's think step-by-step uses a two-stage prompting process:
1. Reasoning Extraction (First Stage)
- Input question is formatted as "Q: [Question]. A: Let's think step by step"
- Model generates step-by-step reasoning
2. Answer Extraction (Second Stage)
- Combines original question, generated reasoning, and answer-extraction prompt
- Uses format-specific triggers like "Therefore, the answer is..."
- Extracts final answer in correct format
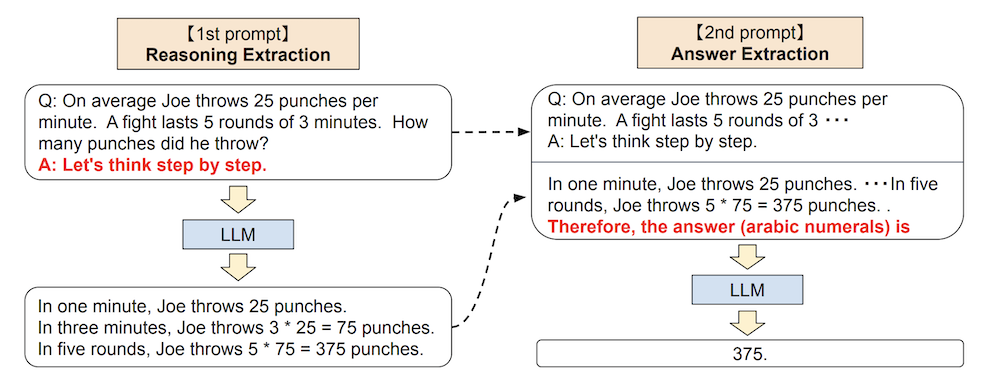
Figure 2: Full pipeline of Zero-shot-CoT as described in section 3.
While this approach requires two prompting steps instead of one, it eliminates the need for carefully engineered examples that traditional few-shot methods require. The method can be used with any decoding strategy, though the researchers used greedy decoding for simplicity. The approach's flexibility comes from its ability to adapt to different answer formats while maintaining the same basic reasoning structure, making it truly task-agnostic.
a) It uses a single prompt to generate both reasoning and answer
b) It requires examples like traditional chain-of-thought prompting
c) It uses two separate prompts - one for reasoning and one for answer extraction
d) It only works with numerical answers
e) It requires fine-tuning the model for each task type
Results
The researchers tested this approach on various tasks including: - Arithmetic reasoning (MultiArith, [[GSM8K]]) - Symbolic reasoning (Last Letter, Coin Flip) - Commonsense reasoning - Logical reasoning
The results were remarkable. For example, on the MultiArith dataset, accuracy increased from 17.7% to 78.7% simply by adding the step-by-step prompt. They showed that CoT helped large models the most.
a) Smaller models performed better with zero-shot CoT
b) Model size had no effect on performance
c) Larger models showed significantly better performance with zero-shot CoT
d) Zero-shot CoT only worked on medium-sized models
Why This Matters
This discovery has several important implications for [[Large Language Models]].
- It suggests that LLMs have inherent reasoning capabilities that can be accessed with the right prompting
- It provides a simpler alternative to few-shot learning for complex tasks
- It hints at broader cognitive capabilities in LLMs that we might not have fully explored
a) LLMs have untapped reasoning capabilities
b) Complex prompting with examples might be unnecessary
c) LLMs need to be retrained to achieve better reasoning
d) Simple prompts can unlock sophisticated behaviors
The research suggests that before investing in creating complex few-shot examples or fine-tuning datasets, we should first explore what capabilities already exist within these models through simple prompting strategies.
This work sets a new baseline for evaluating language models' reasoning capabilities and opens up exciting possibilities for making AI systems more capable through clever prompting rather than just increasing model size or training data.