Negative Log-Likelihood
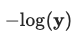
Negative log-likelihood, or NLL, is a Loss Function used in multi-class classification. It measures how closely our model predictions align with the ground truth labels.
It is calculated as −log(ˆy), where ˆy is the prediction corresponding to the true class label after the model outputs are converted into probabilities by applying the Softmax Function to them. The loss for a mini-batch is computed by calculating the NLL for each item and then calculating the mean or sum of all items in the batch.
Since a negative value is returned for the log of a number greater than 0 and less than 1, we add a negative sign to convert it to a positive number, hence negative log-likelihood. At 0 the function returns ∞ (−log(0)=∞) and at 1 returns 0 (−log(1)=0), so very wrong answers are heavily penalised.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(0.01, 1.0, 0.001)
y = -np.log(x)
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6,4))
ax.plot(x,y)
plt.ylabel('-log(x)')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.title('Negative log-likelihood range')
plt.show()
Because the Softmax Function tends to force a single significant number, the loss function only needs to be concerned with the loss corresponding to the correct labels.
In PyTorch, the function is called torch.functional.nll_loss, although it doesn't take the log, as it expects outputs from a LogSoftmax activation layer.
Referred to as Log Loss in binary classification problems.
Code example:
import numpy as np, pandas as pd
from torch import tensor, nn
def softmax(x):
return np.exp(x) / np.exp(x).sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)
labels = [0, 2, 1, 3]
logits = np.array([
[3.5, -3.45, 0.23, 1.25],
[-2.14, 0.54, 2.67, -5.23],
[-1.34, 5.01, -1.54, -1.17],
[ -2.98, -1.37, 1.54,5.23]
])
probs = softmax(logits)
log_probs = np.log(softmax(logits))
nll = -(log_probs[range(len(labels)), labels])
nll
array([0.13484927, 0.11987498, 0.00523357, 0.02625655])
We can check to see that is equal to the output of NLLLoss, with no mean or sum reduction step.
nn.NLLLoss(reduction='none')(tensor(log_probs), tensor(labels))
tensor([0.1348, 0.1199, 0.0052, 0.0263], dtype=torch.float64)
Below the cell is highlighted that corresponds to the correct label.
def style_specific_cell(x):
return ['background-color:#ccc' if i == x.label else '' for i in range(len(x))]
df = pd.DataFrame(probs, columns=['man', 'woman', 'camera', 'tv'])
df['label'] = labels
df['-log(pred)'] = nll
df.style.apply(style_specific_cell, axis=1)
| man | woman | camera | tv | label | -log(pred) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.873848 | 0.000838 | 0.033212 | 0.092103 | 0 | 0.134849 |
| 1 | 0.007227 | 0.105412 | 0.887031 | 0.000329 | 2 | 0.119875 |
| 2 | 0.001738 | 0.994780 | 0.001423 | 0.002060 | 1 | 0.005234 |
| 3 | 0.000265 | 0.001325 | 0.024325 | 0.974085 | 3 | 0.026257 |
Negative Log-Likelihood is the 2nd part of the Categorical Cross-Entropy Loss.
Recommended Reading
Deep Learning for Coders with Fastai and PyTorch: AI Applications Without a PhD

This book is my favourite practical overview of Deep Learning. Learn more about negative log-likelihood in Chapter 6, pg. 231-232.